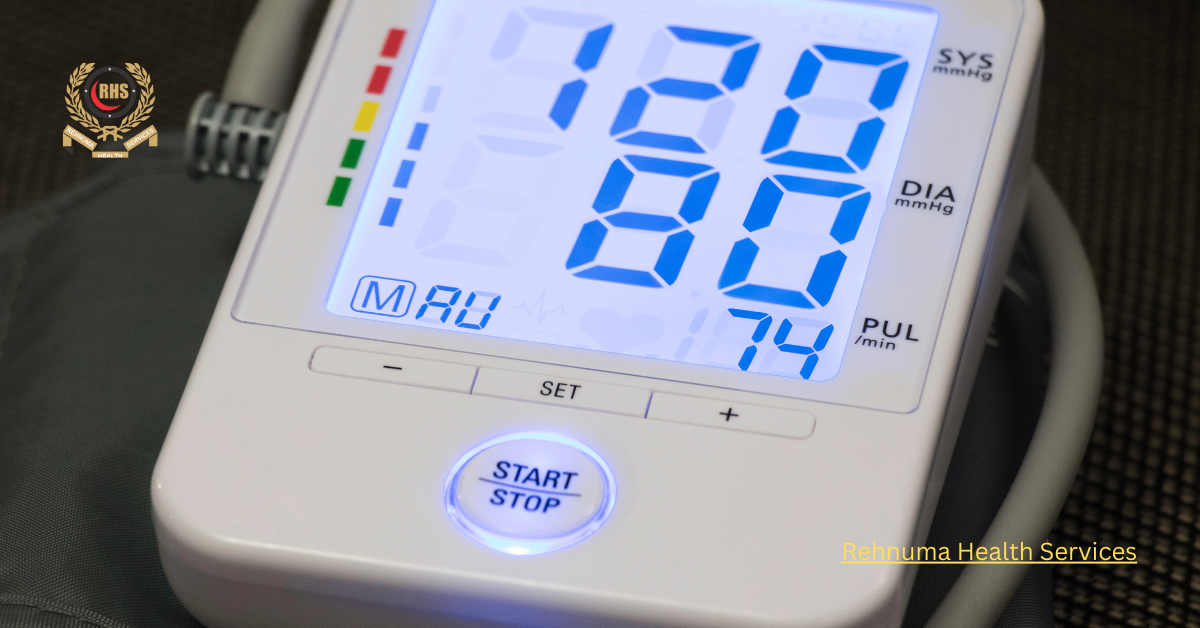
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a critical health concern affecting millions worldwide. Traditional blood pressure monitoring methods often involve periodic visits to healthcare facilities, making continuous monitoring challenging. However, with advancements in technology, remote blood pressure monitoring devices have emerged as a game-changer in managing hypertension effectively and conveniently. This blog delves into the intricacies of remote blood pressure monitoring devices, their benefits, working mechanisms, and their transformative impact on healthcare.
1. Introduction to Remote Blood Pressure Monitoring
Remote blood pressure monitoring devices are innovative tools that enable individuals to measure and track their blood pressure from the comfort of their homes. These devices utilize wireless technology to transmit data to healthcare providers, allowing for continuous monitoring and timely interventions. This remote monitoring approach is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions, elderly individuals, and those living in remote areas.
2. The Importance of Blood Pressure Monitoring
Blood pressure is a critical indicator of cardiovascular health. High blood pressure, if left unmanaged, can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. Regular monitoring is essential to detect any abnormalities early and to manage hypertension effectively. Traditional methods of blood pressure measurement often involve occasional visits to a healthcare provider, which may not provide a comprehensive picture of an individual’s blood pressure fluctuations throughout the day.
3. Evolution of Blood Pressure Monitoring Devices

The evolution of blood pressure monitoring devices reflects significant advancements in medical technology and patient care over the years. Here’s a brief overview of their development:
Traditional Sphygmomanometers
The traditional method of measuring blood pressure involves using a sphygmomanometer, which consists of an inflatable cuff, a measuring unit (mercury manometer or aneroid gauge), and a stethoscope. This method, although accurate, requires a healthcare professional’s presence, making it less convenient for regular monitoring.
Digital Blood Pressure Monitors
Digital blood pressure monitors simplified the process, allowing individuals to measure their blood pressure at home. These devices use oscillometric measurements, where the cuff inflates and deflates automatically, and a digital display shows the readings. While digital monitors provided convenience, they still required manual logging and occasional calibration.
Emergence of Remote Monitoring Devices
The advent of wireless technology paved the way for remote blood pressure monitoring devices. These devices incorporate advanced sensors and wireless connectivity to measure, record, and transmit blood pressure data in real time. This technology allows for continuous monitoring, automatic data logging, and seamless communication with healthcare providers.
4. How Remote Blood Pressure Monitoring Devices Work
Let we explore the working principles of Remote Blood Pressure Monitoring Devices in following points:
Components of Remote Monitoring Systems
Remote blood pressure monitoring devices typically consist of the following components:
- Blood Pressure Cuff: Similar to traditional devices, a cuff is placed around the upper arm to measure blood pressure.
- Sensor and Display Unit: This unit contains sensors to detect blood pressure and a display to show readings.
- Wireless Connectivity: Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or cellular technology enables data transmission to connected devices.
- Mobile Application or Web Portal: A dedicated app or web portal allows users to view and manage their blood pressure data.
- Cloud Storage: Data is stored securely in the cloud, accessible by both patients and healthcare providers.
Measuring and Transmitting Data
When the cuff is inflated, the sensors detect blood pressure readings. These readings are then transmitted wirelessly to the connected mobile device or web portal. The data is stored in the cloud, allowing for real-time monitoring and historical data analysis. Healthcare providers can access this data to monitor trends, make informed decisions, and provide timely interventions.
Benefits of Remote Blood Pressure Monitoring
- Continuous Monitoring: Unlike traditional methods, remote devices enable continuous monitoring, providing a comprehensive view of blood pressure fluctuations.
- Convenience: Patients can measure their blood pressure at any time, eliminating the need for frequent visits to healthcare facilities.
- Early Detection: Continuous monitoring helps detect abnormalities early, allowing for prompt intervention and prevention of complications.
- Data Accuracy: Automated data logging reduces the risk of manual errors, ensuring accurate and reliable records.
- Improved Patient Engagement: Patients can actively participate in their healthcare by regularly monitoring and managing their blood pressure.
- Enhanced Healthcare Provider Support: Real-time data transmission enables healthcare providers to offer personalized care and timely interventions.
5. Types of Remote Blood Pressure Monitoring Devices
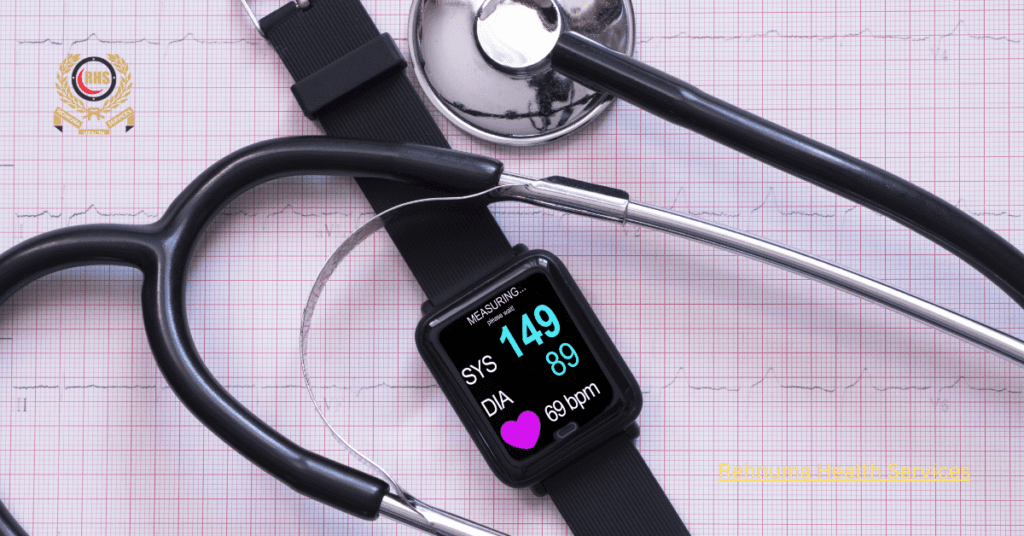
There are the following types of Remote Blood Pressure Monitoring Devices.
Wearable Devices
Wearable blood pressure monitors, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, offer a convenient way to monitor blood pressure on the go. These devices incorporate sensors that measure blood pressure and other vital signs, providing continuous data throughout the day. Wearable devices are particularly beneficial for individuals with active lifestyles.
Home Blood Pressure Monitors
Home blood pressure monitors are designed for use in a stationary setting. These devices typically include an upper-arm cuff and a display unit. They are easy to use and provide accurate readings, making them ideal for daily monitoring. Some models come with advanced features such as irregular heartbeat detection and multi-user functionality.
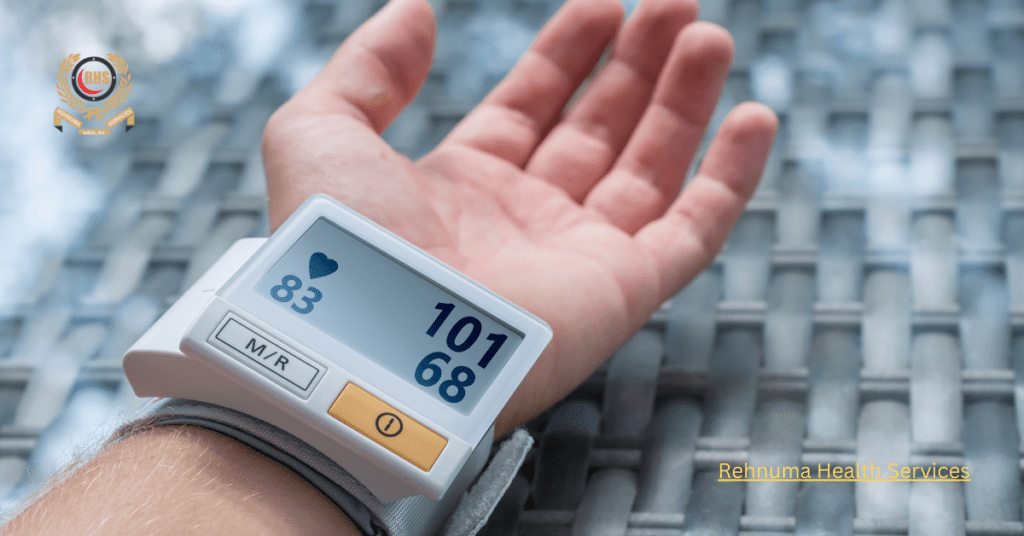
Smartphone-Connected Monitors
Smartphone-connected monitors use Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to connect to a mobile app. The app displays the readings, stores data, and provides insights into blood pressure trends. These monitors offer the advantage of seamless data integration with other health apps and devices, creating a comprehensive health monitoring ecosystem.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitors
Ambulatory blood pressure monitors are designed for continuous monitoring over a 24-hour period. These devices are worn on the body and take measurements at regular intervals. They provide a detailed picture of blood pressure variations throughout the day and night, offering valuable insights into nocturnal hypertension and white-coat syndrome.
6. Implementing Remote Blood Pressure Monitoring in Healthcare
There are many implementation of remote blood pressure monitoring in healthcare department.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR)
To maximize the benefits of remote blood pressure monitoring, seamless integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR) is essential. EHR integration allows healthcare providers to access patient data in real time, facilitating informed decision-making and personalized care plans. Data interoperability between monitoring devices and EHR systems enhances the overall efficiency of hypertension management.
Telemedicine and Remote Consultations
Remote blood pressure monitoring complements telemedicine by providing real-time data during virtual consultations. Patients can share their readings with healthcare providers, enabling accurate diagnosis and treatment adjustments without the need for in-person visits. Telemedicine platforms with integrated monitoring capabilities offer a holistic approach to hypertension management.
Personalized Treatment Plans
The continuous stream of data from remote monitoring devices allows healthcare providers to create personalized treatment plans based on individual trends and patterns. By analyzing the data, providers can identify triggers, adjust medications, and recommend lifestyle modifications tailored to each patient’s needs. This personalized approach enhances treatment efficacy and patient adherence.
7. Challenges and Considerations
There are the following challenges and considerations in Remote Blood Pressure Devices in healthcare.
Data Privacy and Security
The transmission and storage of sensitive health data pose significant privacy and security challenges. Ensuring that remote monitoring devices and platforms comply with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is crucial. Robust encryption, secure cloud storage, and user authentication mechanisms are essential to protect patient data.
Device Accuracy and Reliability
The accuracy and reliability of remote blood pressure monitoring devices are paramount for effective hypertension management. Regular calibration, quality control, and adherence to medical device standards are necessary to ensure precise measurements. Healthcare providers should recommend FDA-approved devices with proven accuracy and reliability.
Patient Education and Compliance
Successful implementation of remote blood pressure monitoring requires patient education and compliance. Patients need to understand how to use the devices correctly, interpret the readings, and follow healthcare providers’ recommendations. User-friendly interfaces, instructional materials, and regular follow-ups can enhance patient engagement and adherence.
Integration Challenges
Integrating remote monitoring data with existing healthcare systems can be complex. Interoperability standards, data exchange protocols, and seamless integration with EHR systems are essential to avoid data silos and ensure a unified view of patient health. Collaborative efforts between device manufacturers, healthcare providers, and IT experts are necessary to address integration challenges.
8. Future Trends in Remote Blood Pressure Monitoring
Remote blood pressure monitoring is rapidly evolving with advancements in technology and healthcare practices. Here are some future trends to watch for:
Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics have the potential to revolutionize remote blood pressure monitoring. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict hypertension risks, and provide personalized recommendations. Machine learning models can also enhance the accuracy of measurements and detect anomalies in real-time.
Integration with Wearable Health Ecosystems
The future of remote blood pressure monitoring lies in its integration with comprehensive wearable health ecosystems. Wearable devices that monitor multiple vital signs, such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity, can provide a holistic view of an individual’s health. This integration enables proactive health management and early intervention.
Enhanced Patient Engagement through Gamification
Gamification techniques can improve patient engagement and adherence to monitoring routines. Incorporating elements such as rewards, challenges, and progress tracking into mobile apps can motivate patients to regularly monitor their blood pressure. Gamification fosters a sense of accomplishment and encourages long-term compliance with healthcare regimens.
Remote Monitoring in Clinical Trials
Remote blood pressure monitoring devices are poised to play a significant role in clinical trials. These devices enable continuous data collection, reducing the need for frequent clinic visits and enhancing the accuracy of trial outcomes. Remote monitoring can also improve patient recruitment and retention by offering a convenient and non-invasive method of data collection.
Conclusion
Remote blood pressure monitoring devices are transforming hypertension management by providing continuous, accurate, and convenient monitoring solutions. These devices empower patients to take control of their health, enable early detection of abnormalities, and facilitate personalized treatment plans. While challenges such as data privacy, device accuracy, and integration exist, the future of remote blood pressure monitoring holds immense promise. With advancements in AI, wearable health ecosystems, and patient engagement strategies, remote monitoring is set to revolutionize healthcare and improve outcomes for individuals with hypertension. Embracing this technology is a crucial step toward a healthier future.
FAQs
What is remote blood pressure monitoring?
Remote blood pressure monitoring is a healthcare approach where patients measure their blood pressure at home using digital devices. These devices are equipped with technology that allows the readings to be transmitted electronically to healthcare providers for review and management.
Can blood pressure be taken remotely?
Yes, most remote monitoring systems use encrypted data transmission methods to ensure patient information remains confidential and secure.
Which is the best blood pressure monitoring device?
Omron Platinum Blood Pressure Monitor is often considered one of the best blood pressure monitors due to its accuracy, ease of use, and advanced features like Bluetooth connectivity and a multi-user mode.
What are the different types of blood pressure monitoring devices?
Manual Blood Pressure Monitors: These include a cuff, a squeeze bulb, and a stethoscope. They are typically used by healthcare professionals.
Digital Blood Pressure Monitors: These are electronic devices that inflate the cuff and provide a digital readout of your blood pressure. They are user-friendly and suitable for home use.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitors: These are portable devices worn throughout the day to continuously monitor blood pressure.
Wrist Blood Pressure Monitors: These are similar to digital monitors but are worn on the wrist. They are more portable but can be less accurate than upper arm monitors.
Finger Blood Pressure Monitors: These are compact and easy to use but are generally less accurate and not commonly recommended.
What is a remote monitoring system?
A remote monitoring system allows healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health data remotely using connected devices. These systems collect data from various health monitoring devices, such as blood pressure monitors, glucose meters, and wearable fitness trackers, and transmit the data to healthcare providers for real-time analysis and intervention.
How can I monitor my BP at home?
Choose the Right Device: Select a reliable and accurate blood pressure monitor.
Follow Instructions: Read the manual carefully to understand how to use the device.
Proper Positioning: Sit in a comfortable position with your back supported. Place your arm at heart level.
Take Readings at the Same Time Daily: To get consistent readings, measure your BP at the same time each day.
Record Readings: Keep a log of your readings to track changes and share with your healthcare provider.
Avoid Certain Activities: Before taking a reading, avoid eating, smoking, or exercising for at least 30 minutes.
Is a digital BP machine accurate?
Yes, digital blood pressure machines are generally accurate, especially upper arm monitors. However, accuracy can vary depending on the device’s quality and whether it is used correctly. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and ensure the cuff fits properly. Regular calibration and validation against a manual device by a healthcare professional can also help maintain accuracy.
What is the normal BP range?
The normal blood pressure range for most adults is:
Diastolic (Bottom Number): 60 to 80 mmHg
Systolic (Top Number): 90 to 120 mmHg